What is Six Sigma? And the benefits of Lean Six Sigma.
WHAT IS SIX SIGMA?
Six Sigma is a method that provides organizations tools to improve the capability of their business processes. This increase in performance and decrease in process variation helps lead to defect reduction and improvement in profits, employee morale, and quality of products or services.
“Six Sigma quality” is a term generally used to indicate a process is well controlled (within process limits ±3s from the center line in a control chart, and requirements/tolerance limits ±6s from the center line).
DIFFERING OPINIONS ON THE DEFINITION OF SIX SIGMA
The differing definitions below have been proposed for Six Sigma, but they all share some common threads:
- The use of teams that are assigned well-defined projects that have a direct impact on the organization’s bottom line.
- Training in “statistical thinking” at all levels and providing key people with extensive training in advanced statistics and project management. These key people are designated “Black Belts.”
- Emphasis on the DMAIC approach to problem solving: define, measure, analyze, improve, and control.
- A management environment that supports these initiatives as a business strategy.
Philosophy: The philosophical perspective of Six Sigma views all work as processes that can be defined, measured, analyzed, improved, and controlled. Processes require inputs (x) and produce outputs (y). If you control the inputs, you will control the outputs. This is generally expressed as y = f(x).
Set of tools: The Six Sigma expert uses qualitative and quantitative techniques or tools to drive process improvement. Such tools include statistical process control (SPC), control chart, failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), and process mapping. Six Sigma professionals do not totally agree as to exactly which tools constitute the set.
Methodology: This view of Six Sigma recognizes the underlying and rigorous DMAIC approach. DMAIC defines the steps a Six Sigma practitioner is expected to follow, starting with identifying the problem and ending with the implementation of long-lasting solutions. While DMAIC is not the only Six Sigma methodology in use, it is certainly the most widely adopted and recognized.
Metrics: In simple terms, Six Sigma quality performance means 3.4 defects per million opportunities (accounting for a 1.5-sigma shift in the mean).
Six Sigma Quality Performance
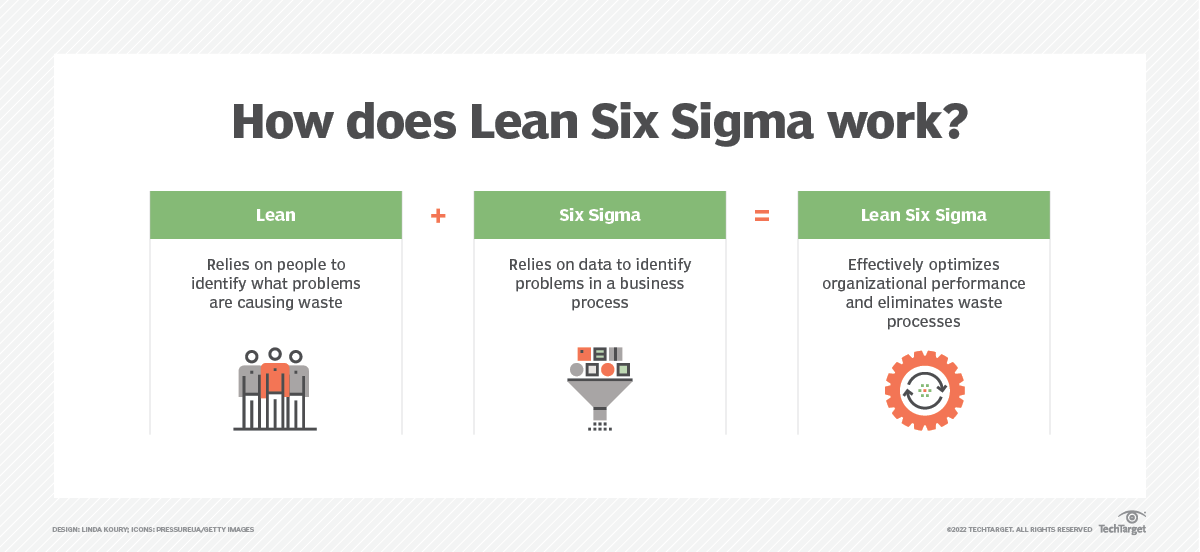
What is Lean Six Sigma
Six Sigma focuses on reducing process variation and enhancing process control, whereas lean drives out waste (non-value added processes and procedures) and promotes work standardization and flow. The distinction between Six Sigma and lean has blurred, with the term “lean Six Sigma” being used more and more often because process improvement requires aspects of both approaches to attain positive results.
Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-driven philosophy of improvement that values defect prevention over defect detection. It drives customer satisfaction and bottom-line results by reducing variation, waste, and cycle time, while promoting the use of work standardization and flow, thereby creating a competitive advantage. It applies anywhere variation and waste exist, and every employee should be involved.
INTEGRATING LEAN AND SIX SIGMA
Lean and Six Sigma both provide customers with the best possible quality, cost, delivery, and a newer attribute, nimbleness. There is a great deal of overlap between the two disciplines; however, they both approach their common purpose from slightly different angles:
• Lean focuses on waste reduction, whereas Six Sigma emphasizes variation reduction.
• Lean achieves its goals by using less technical tools such as kaizen, workplace organization, and visual controls, whereas Six Sigma tends to use statistical data analysis, design of experiments, and hypothesis testing.
Often successful implementations begin with the lean approach, making the workplace as efficient and effective as possible, reducing waste, and using value stream maps to improve understanding and throughput. If process problems remain, more technical Six Sigma statistical tools may then be applied.
Why is Lean Six Sigma important?
There are many stories of businesses seeing consistent, measurable improvements in operations from using the Lean Six Sigma methods. The combination of process streamlining through a data-driven approach is a solid business plan.
What is the history of Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is the combination of two methodologies. The first is Lean, developed by Toyota in the 1940s to streamline operational processes in the manufacturing and sale of cars.
Six Sigma was developed in the 1980s by Motorola and is inspired by Japan’s Kaizen model. It seeks to identify and reduce defects in the production process.
What is the Lean Six Sigma Core Concept?
Lean focuses on the reduction and elimination of eight kinds of waste. These are identified by the acronym DOWNTIME (defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and extra-processing). Any method, measure or tool that helps to identify or eliminate waste can be part of the lean methodology. Among those tools are:
- The 5 Whys: This was also made popular by Toyota in the 1950s. It’s a pretty simple process–whenever a problem arises, just ask “Why?” Then keep asking why until you get to a solution. At least five times or more.
- Kanban Inventory Control Cues: This involves using visual tools to keep track of work as it moves through a process.
- Heijunka Box: This is a full wall-sized scheduling tool. It’s a grid formation where boxes called pigeonholes are items in process. The rows represent the process and the column is the time.
- Ishikawa Fishbone Diagrams: This visual tool identifies cause and effect to help in determining reasons behind problems.
- Takt Time Calculations: This formula identifies the maximum acceptable time to meet demands of the customer.
Six Sigma is about process improvement. Six Sigma uses the acronym DMAIC to explain their data-driven five-step method. DMAIC stands for define, measure, analyze, improve and control.
These two ways of focusing work meld together to form the core concept of Lean Six Sigma. Let’s look at how this happens.
What are the techniques of Lean Six Sigma?
- Kanban practices which include work visualization and limited work in progress maximize efficiency and encourage continuous improvement.
- Kaizen stresses self-development and ongoing improvement by team members to facilitate overall operational improvement.
- Value stream mapping helps bring into focus places for eliminating waste and optimizing processes.
- The 5S tool ensures that work environments are efficient, productive, safe and produce results.
What are the Lean Six Sigma phases?
The Lean Six Sigma phases are taken from the Six Sigma methodology (DMAIC).
- Define: Define the problem from all points of view–the company perspective, the stakeholder perspective and the customer perspective.
- Measure: Examine the problem and evaluate how it contributes to solving the problem. Tract actual performance data to support measurements.
- Analyze: The team performs data analysis, process analysis, and root-cause analysis.
- Improve: Solve the problem and then verify the improvement that occurred. Data justifies that the solution fits the issue.
- Control: Continuously monitor improvement and accelerate improvement where possible.
What are Lean Six Sigma Belt Levels?
Lean Six Sigma uses five belt levels to denote the various stages of expertise. This may vary slightly depending on the organization doing the certification.
- White Belt: A white belt means an employee understands the basic meaning and goals of Lean Six Sigma.
- Yellow Belt: A yellow belt means an employee understands essential Lean Six Sigma concepts, tools and techniques.
- Green Belt: A green belt verifies that an employee has a level of expertise in Lean Six Sigma and can launch and manage Lean Six Sigma projects.
- Black Belt: A black belt employee has advanced Lean Six Sigma expertise and reports to Master Black Belts. They can be full-time, cross-functional project leaders and also coach and mentor Green Belts.
- Master Black Belt: Achieving a Master Black Belt has extensive Lean Six Sigma expertise and is typically responsible for the overall Lean Six Sigma initiative. They can mentor other belt levels and manage projects.
What are the benefits of Lean Six Sigma?
- Lean Six Sigma increases the efficiency of important processes. Through this, companies can improve the working environment for employees and the customer experience as well.
- By streamlining and simplifying processes, companies can have more control and adapt more quickly to new opportunities.
- Streamlining can lead to increased revenue, reduced costs and more business opportunities.
- Increasing employee skill levels can benefit all aspects of the organization and foster better employee engagement and loyalty.
- Better methods of preventing defects saves time, money and human effort which would have taken longer to resolve.
The end goal is to reduce waste and improve performance by tracking all data associated with project processes. This will result in customers, employees and companies who are more satisfied.
Sources:
https://asq.org/quality-resources/six-sigma
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/l/lean-six-sigma.asp
https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/lean-Six-Sigma
Tag:DMAIC, Quality Management





3 Comments
Thanks for your blog, nice to read. Do not stop.
Interesting PMP Certification course with Bruce Wehrle, who is a great experienced instructor, very supportive and providing interactive and insightful training. I was satisfied with overall experience and would definitely recommend the course and instructor to my peers.
Thank you! This helps a lot!